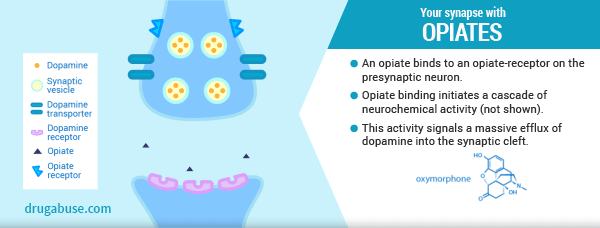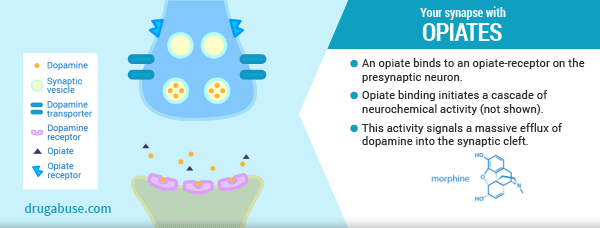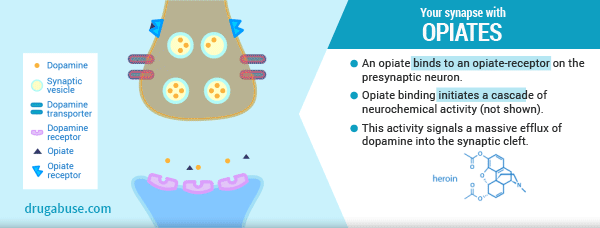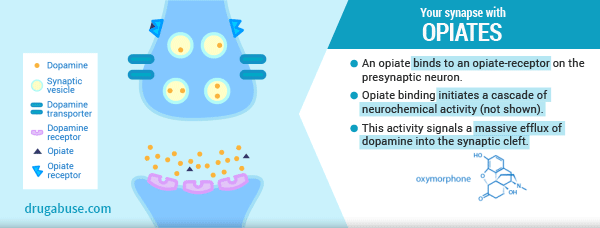
In our last post we explored the neurological changes that occur in the brain when a person misuses opiates (heroin or prescription pain pills). We learned that the brain’s natural endorphin system shuts down and becomes dependent on an external source, such as heroin or prescription narcotics. We also learned the body requires endorphins to function normally; to manage pain, energy, and mood. So, an individual MUST continue using because it is a physiological necessity.
If a diabetic requires a medication to correct an internal imbalance, they would have the needed support from friends and family to do whatever they needed to do to get better. Yet, there is so much stigma, due to lack of understanding about the nature or opiate dependency, that creates unnecessary barriers to people getting the help they need, especially help that is proven to be the most effective form of treatment for this particular condition.
So how does one break the need to use opiates once these changes occur?
Methadone and Suboxone are both medications that can be prescribed to manage opiate withdrawals and craving while the brain begins the process of rebuilding its internal endorphin workforce.
Methadone is a full agonist opiate, meaning it has the potential to act like any other opiate. It has the potential to satisfy withdrawals and cravings but also has an abuse potential. Suboxone has less risk involved but is expensive and doesn’t work for everyone.
Methadone
Methadone is a synthetic opiate that sits in the brain’s opiate receptors. When prescribed a therapeutic dose, methadone will sit in the opiate receptor and do the necessary jobs of preventing withdrawal, stifling cravings, provide energy, stabilize mood, and manage pain, just like the natural endorphins will eventually begin doing again.
The length of time it takes each person’s brain to fully recovery varies based on many variable, such as; length of time using drugs, quantity and quality of the drugs consumed frequency of consumptions, personal physiology, psychological state, level of physical activity, nutrition, sleep habits, and recovery support.
There is the potential for abuse but if managed well this can be avoided. The methadone clinic providing the medication should always strive for conservative dosing (prevent withdrawal without sedation), random drug screens, diversionary practices, laboratory testing, and ensuring there is adequate recovery capital before allowing take homes.
Methadone tends to work better for individuals with a chronic opiate use disorder. These individuals are more likely to thrive when they have controlled dosing, daily engagement at the clinic, accountability and encouragement, case management and counseling.
Suboxone
Suboxone tends to work better for individuals who already have some measure of recovery capital. These individuals also are more likely to have jobs, transportation, stable housing, and supportive relationships. These individuals are also more likely to have used prescription narcotics vs. street heroin, although some long time users report significant benefits from using Suboxone.
Suboxone is a partial agonist, which means it only does part of the job of an opiate. There are two medications combined to make up Suboxone, the first is Buprenorphine. It will sit in the brain’s opiate receptors but won’t activate the brain’s pleasure/reward center. This is good news because that means there is very little chance of misusing this medication. It also has built in protective factors. There is a ceiling to how much Suboxone you can take. There is a max dose a person can take before they stop receiving benefit from the medication. This reduces the potential for using the medication to “get high”.
There is also naloxone in the medication. This is the same medication they give to someone who overdose on opiates. It is more commonly known as NARCAN. NARCAN, when introduced to the body with “kick” the opiates out of the opiate receptors and reverse an over dose (we’ll talk about NARCAN in greater detail in a future post). If someone on Suboxone tries to misuse this medication or, they try to use other opiates while on the medication, it has the potential to send them into immediate withdrawal. Because of this, there is very little risk that the individual will be able to misuse or abuse the Suboxone.
Because there is less while on Suboxone the consumer has a tendency to stabilize fairly quickly. Methadone takes slightly longer as the individual and treatment team work to establish a therapeutic dose by adjusting the medication over time.
The likelihood of an individual in severe withdrawal engaging in treatment, rebuilding relational trust, or going to work or caring for the kids is very low, if not nearly impossible. There will always be exceptions to this but it is not the norm. The brain will eventually begin to rebuild its own endorphin system and in time, many are able to taper off these medication altogether. There are a number of people who have used in such a way that their brain will never fully recover and will require medication for the remainder of their life.
So, once an individual becomes stable on medication, what does effective treatment for the opiate dependent individual look like. We’ll explore that in our next post.